(NewsBERT)Distilling Pre-trained Language Model for Intelligent News Application 论文笔记

知识蒸馏(KD)
知识蒸馏是一种 模型压缩 方法,是一种基于 teacher-student 的训练方法,具体而言就是将已经训练好的模型包含的知识(Knowledge),蒸馏(Distill)提取到另一个模型里面去,其本质就是模型压缩
Teacher-Student
应用场景
分类问题,即原始模型中,对于输入X,其都能输出Y,其中Y经过softmax 的映射,输出值对应相应类别的概率值。(在保证小模型和大模型相似的基础上,重新构建输入与输出之间的映射关系)
训练方法
采用的直白且高效的迁移泛化能力的方法是:使用 softmax 层输出的类别概率向量作为“soft target”,即对比KD的训练过程和传统的训练过程为:
- 传统training过程(hard targets): 对ground truth求极大似然
- KD的training过程(soft targets): 用large model的class probabilities作为soft targets
相比于传统的训练过程,KD的训练更能学到负标签中的信息,比如某些负标签对应的概率远远大于其他负标签。而在传统的训练过程(hard target)中,所有负标签都被统一对待。也就是说,KD的训练方式使得每个样本给Net-S带来的信息量大于传统的训练方式。
蒸馏温度T
将原先的softmax函数: \[ q_{i}=\frac{\exp \left(z_{i}\right)}{\sum_{j} \exp \left(z_{j}\right)} \] 加入蒸馏温度变为: \[ q_{i}=\frac{\exp \left(z_{i} / T\right)}{\sum_{j} \exp \left(z_{j} / T\right)} \] 原来的softmax函数是T = 1的特例。 T越高,softmax的output probability distribution越趋于平滑,其分布的熵越大,负标签携带的信息会被相对地放大,模型训练将更加关注负标签。
模型结构
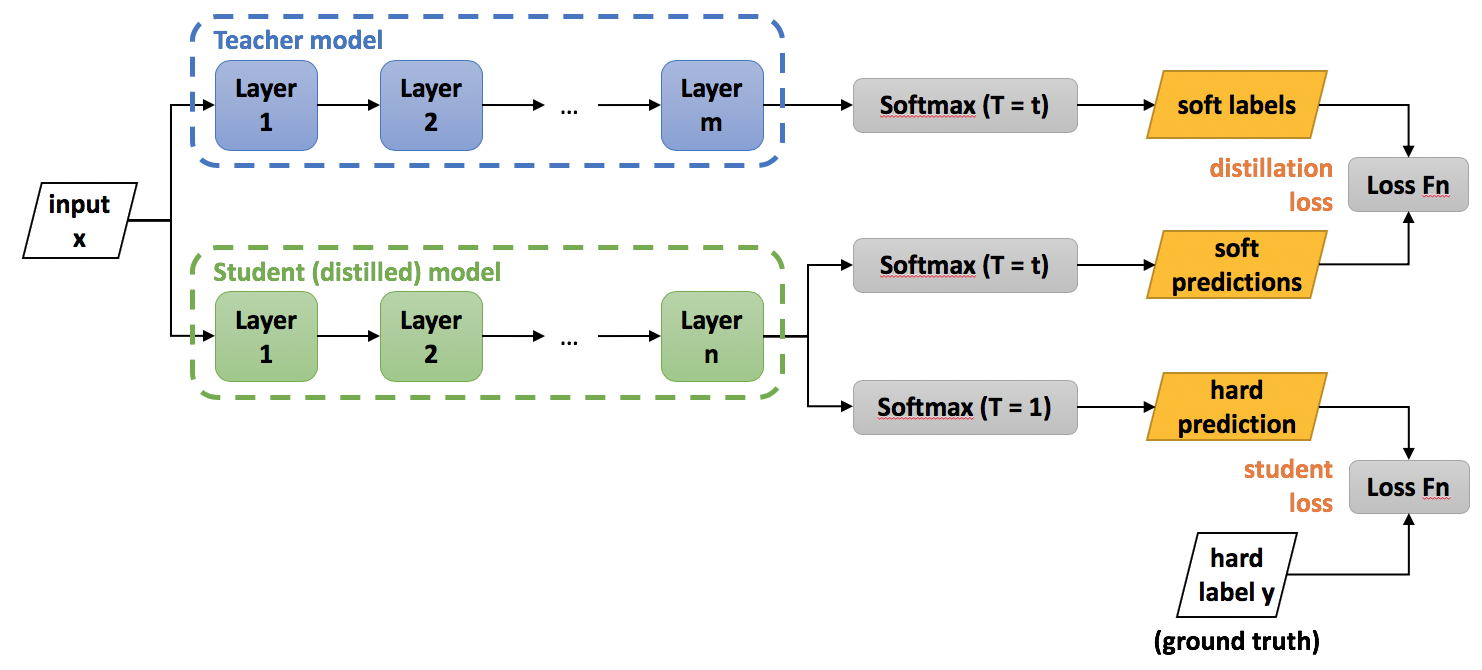
total Loss: \[ L=\alpha L_{\text {soft }}+\beta L_{\text {hard }} \] 对应于图中即为: \[ L=\alpha L_{\text {distillation loss}} + \beta L_{\text {student loss}} \] 其中: \[ \begin{gather} L_{s o f t}=-\sum_{j}^{N} p_{j}^{T} \log \left(q_{j}^{T}\right) \\ p_{i}^{T}=\frac{\exp \left(v_{i} / T\right)}{\sum_{k}^{N} \exp \left(v_{k} / T\right)}, \quad q_{i}^{T}=\frac{\exp \left(z_{i} / T\right)}{\sum_{k}^{N} \exp \left(z_{k} / T\right)} \end{gather} \]
训练技巧
注意:\(\alpha\), \(\beta\) 和 T 均为超参数
- \(L_{\text {soft }}\)的梯度是 \(L_{\text {hard }}\) 梯度的 \(\frac{1}{T^{2}}\) ,因此第一部分Loss占的比重应该增大
- 温度T的选取:
- Net-S参数量比较大 --> 能够学习相对多的信息 --> 从有部分信息量的负标签中学习 --> 温度要高一些
- Net-S参数量比较小 --> 能够学习相对少的信息 --> 防止受负标签中噪声的影响 --> 温度要低一些
现存的问题
- 预训练的语言模型,如BERT和GPT,存在如下问题:参数过多,导致存储占用过大;模型过大,导致推理速度过慢。因此一般无法应用到需要线上快速响应的新闻推荐领域
- 现在的预训练语言模型都是基于维基百科中的一般性语料得到的,不具有领域性,例如在新闻文本提取领域的表现效果不一定是最优的
- 对比之前的知识蒸馏方式,本论文认为
- 之前的方式student模型都是从teacher模型的结果中进行学习,teacher模型的学习经验(learning experience)也是值得学习的
- teacher模型无法感知student模型的学习状态
论文的方法
提出协同训练的student-teacher模型,student模型从teacher模型的学习经验(learning experience)中进行学习
we design a teacher-student joint learning and distillation framework to collaboratively learn both teacher and student models in news intelligence tasks by sharing the parameters of top layers, and meanwhile distill the student model by regularizing the output soft probabilities and hidden representations.
我们提出了一种动量蒸馏法(momentum distillation method),即:
incorporating the gradients of teacher model into the update of student model to better transfer useful knowledge learned by the teacher model.
模型
整体包含三个特点:
- student模型和teacher模型的协同训练,通过设计一个总体的Loss来实现
- student模型和teacher模型共享一些层的参数,使得teacher能够感知student的学习状态
- teacher模型将学习经验传递给student模型,即student模型的梯度结合了teacher模型的梯度
student模型和teacher模型的协同训练
通过下图我们可以看出,student模型设计的初衷是:
- 每一层和teacher模型的结构都相同
- 每一层对应于teacher模型的K层
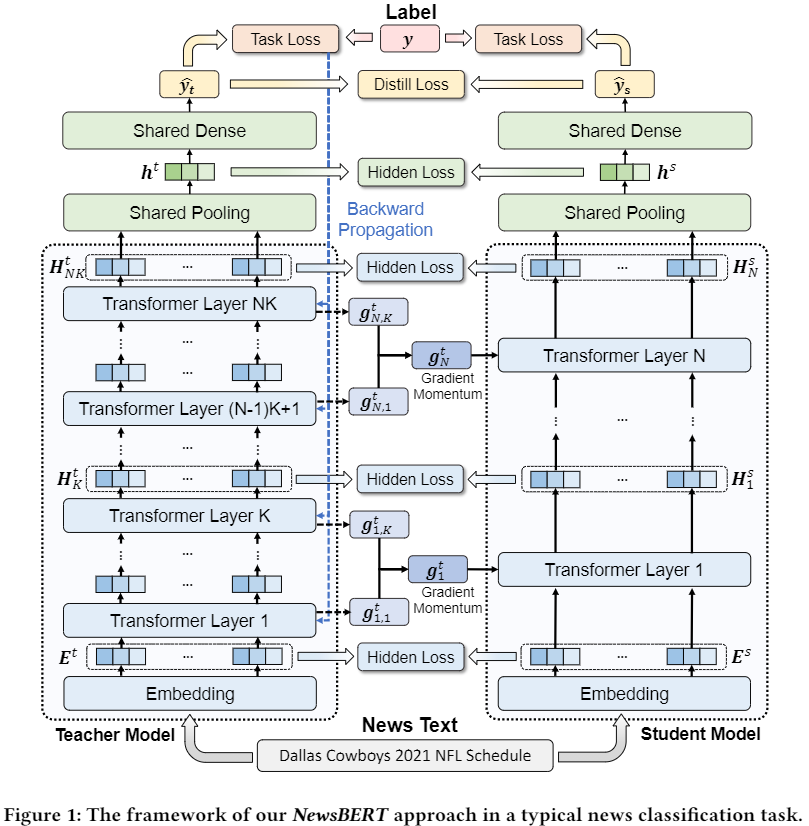
student模型的Loss设计
\[ \mathcal{L}^{s}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}, \Theta_{p}, \Theta_{d}\right)=\mathcal{L}_{d}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}, \Theta_{p}, \Theta_{d}\right)+\operatorname{CE}\left(\hat{y}_{s}, y\right) \]
其中: \[ \mathcal{L}_{d}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}, \Theta_{p}, \Theta_{d}\right)=\mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{l}+\mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{p}+\mathcal{L}_{\text {distill }} \] 其中distill loss(soft loss)为对于soft labels的cross entropy,即: \[ \mathcal{L}_{\text {distill }}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}, \Theta_{p}, \Theta_{d}\right)=\operatorname{CE}\left(\hat{y}_{t} / t, \hat{y}_{s} / t\right) \] \(\mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{l}\)代表中间层和embedding层的MSE值: \[ \mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{l}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}\right)=\operatorname{MSE}\left(\mathrm{E}^{t}, \mathrm{E}^{s}\right)+\sum_{i=1}^{N} \operatorname{MSE}\left(\mathrm{H}_{i K}^{t}, \mathrm{H}_{i}^{s}\right) \] \(\mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{p}\)代表最后pooling层的MSE值: \[ \mathcal{L}_{\text {hidden }}^{p}\left(x, \Theta_{t} ; \Theta_{s}, \Theta_{p}\right)=\operatorname{MSE}\left(\mathrm{h}^{t}, \mathrm{~h}^{s}\right) \]
teacher模型的Loss设计
只计算最后的hard target之间的Loss \[ \mathcal{L}^{t}\left(x ; \Theta_{t}, \Theta_{p}, \Theta_{d}\right)=\operatorname{CE}\left(\hat{y}_{t}, y\right) \]
student模型和teacher模型共享参数
共享了最后的pooling层和dense层
teacher模型给student模型传递学习经验
将teacher的梯度: \[ \mathrm{g}_{i}^{t}=\frac{1}{K} \sum_{j=1}^{K} \mathrm{~g}_{i, j}^{t} \] 传递给student模型: \[ \mathrm{g}_{k}^{s}=\beta \mathrm{g}_{k}^{t}+(1-\beta) \mathrm{g}_{k}^{s} \] 其中\(\beta\)是超参数
训练
- 用teacher模型的前1,2,4层来初始化student模型
- 将来两个模型同时在news domain的语料库上进行训练
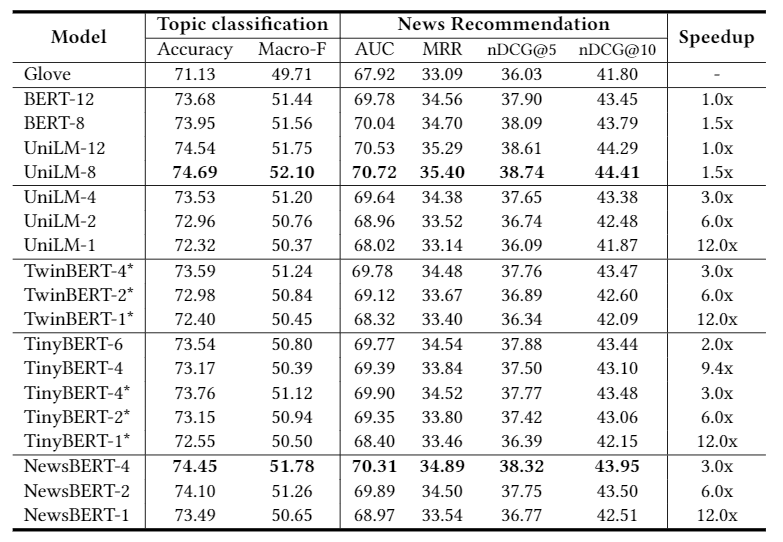
结果
Reference
[1] Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
(NewsBERT)Distilling Pre-trained Language Model for Intelligent News Application 论文笔记
https://xdren69.github.io/2021/04/06/textRepresent-newsBERT/