(RippleNet)Propagating User Preferences on the Knowledge Graph for Recommender Systems 论文笔记
RippleNet: Propagating User Preferences on the Knowledge Graph for Recommender Systems
Intro
现在的基于知识图谱的推荐系统基本上分成两种方法,即:
- embedding-based methods: 利用知识图谱中目标entity周围的entity的embedding的信息来丰富单个entity的信息,一般使用GCN算法或者GAT算法
- path-based methods: 一般需要人工设计meta-path/meta-graph,因此模型学习效果的好坏很大程度依赖于meta-path/meta-graph的设计,并且meta-path/meta-graph很难在学习的过程中被优化
而RippelNet将两者相结合,既考虑了embedding的问题,又考虑了path的问题。解决这一问题的方法被称为preference propagation,借助KG,更加有利于发现用户的高层潜在兴趣。
For each user, RippleNet treats his historical interests as a seed set in the KG, then extends the user’s interests iteratively along KG links to discover his hierarchical potential interests with respect to a candidate item.
模型
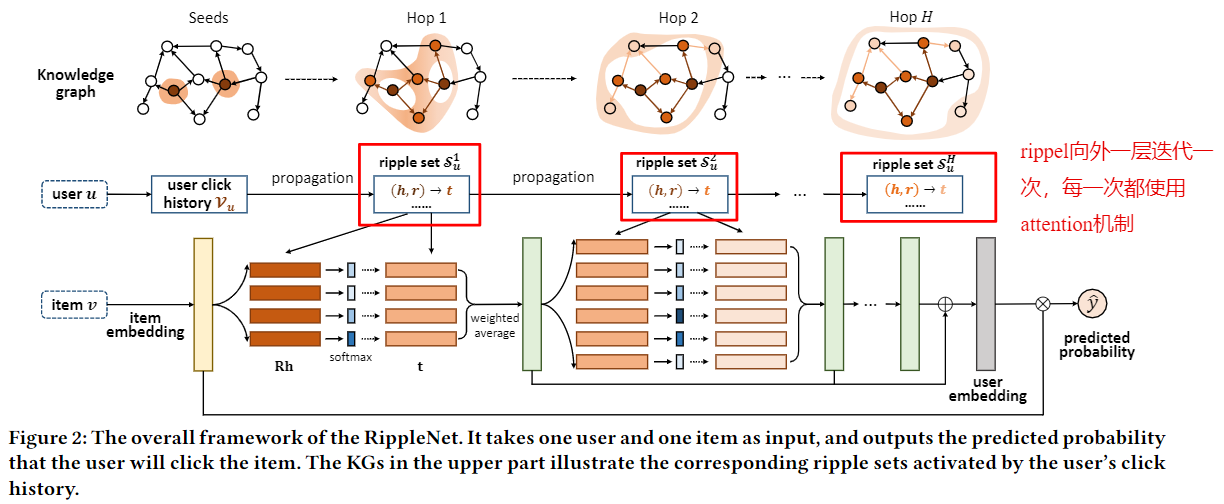
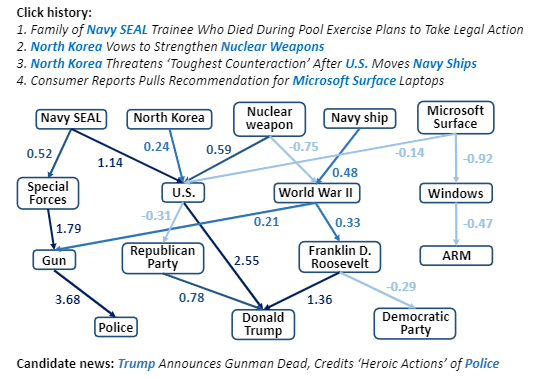
对于一次点击历史中的一个实体,其知识图谱中的rippel如下所示:
对于每一次迭代的entity的集合定义如下: \[ \mathcal{E}_{u}^{k}=\left\{t \mid(h, r, t) \in \mathcal{G} \text { and } h \in \mathcal{E}_{u}^{k-1}\right\}, \quad k=1,2, \ldots, H \] 其中: \[ \mathcal{E}_{u}^{0}=\mathcal{V}_{u}=\left\{v \mid y_{u v}=1\right\} \] 即一开始的seed集合是一个用户所有点击的历史记录中的item对应的entity
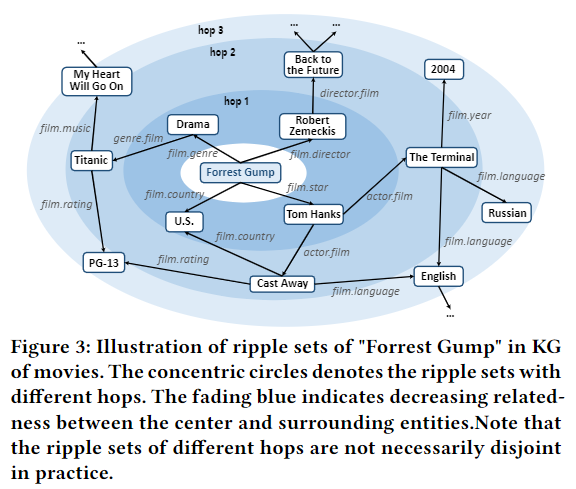
以第一轮rippel传播为例
每一个传播到的entity对应的权重的计算方式如下: \[ p_{i}=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{T}} \mathbf{R}_{i} \mathbf{h}_{i}\right)=\frac{\exp \left(\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{T}} \mathbf{R}_{i} \mathbf{h}_{i}\right)}{\sum_{(h, r, t) \in \mathcal{S}_{u}^{1}} \exp \left(\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{T}} \mathrm{Rh}\right)} \] 每一轮传播过后得到的用户表示(局部)为: \[ \mathbf{o}_{u}^{1}=\sum_{\left(h_{i}, r_{i}, t_{i}\right) \in \mathcal{S}_{u}^{1}} p_{i} \mathbf{t}_{i} \] 最后通过局部用户表示得到的全局用户表示为: \[ \mathbf{u}=\mathbf{o}_{u}^{1}+\mathbf{o}_{u}^{2}+\ldots+\mathbf{o}_{u}^{H} \] 点击率预测方法为: \[ \hat{y}_{u v}=\sigma\left(\mathbf{u}^{\mathrm{T}} \mathbf{v}\right) \]
特殊
- 使用了Memory Networks
实验结果
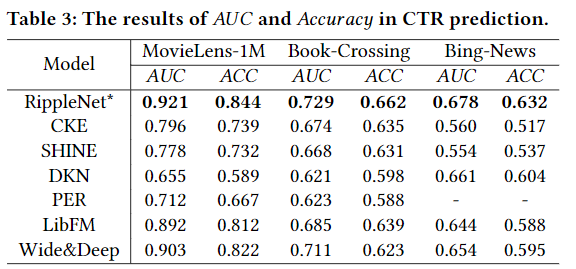
对于baseline的实验
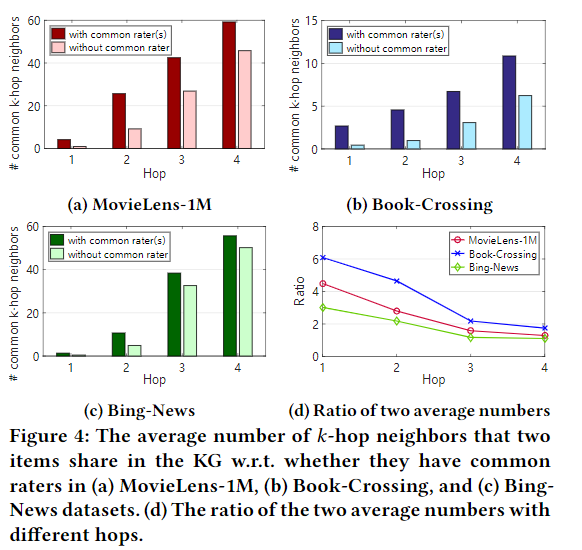
对于hop number的实验
case study
future work
- further investigate the methods of characterizing entity-relation interactions;
- design non-uniform samplers during preference propagation to better explore users’ potential interests and improve the performance.
(RippleNet)Propagating User Preferences on the Knowledge Graph for Recommender Systems 论文笔记