Leveraging Demonstrations for Reinforcement Recommendation Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs 论文阅读
Leveraging Demonstrations for Reinforcement Recommendation Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs
模型整体是基于user-item之间的path来提升推荐的准确性和可解释性的。
整个方法分类两个部分,首先构建一些不完整、不全面的path,来引导随后的ADAC模型来学习一些path;随后通过ADAC模型来学习path
Demonstration Extraction
用来通过Meta-heuristics产生一些样例,可供后面的模型进行学习
首先,我们在设计元启发规则时,应当考虑三个方面的特性:
- Accessibility:通过最小的标签努力可以获得样例
- Explainability:要比随机采样的path更具有解释性
- Accuracy:样例要能够连接已观测到的user-item之间的交互
我们得到的启发式规则如下:
- Shortest path:多条路径时,使用Dijkstra算法寻找最短路径
- Meta-path:设计几条meta-path用于之后的识别
- Path of interest:通过path中用户感兴趣的entity的个数;来判断
meta-path的理解:
\(B o b \stackrel{\text { Purchase }}{\longrightarrow}\) Revolution 5 Running Shoe\(\frac{\text {Produced_By}}{\longrightarrow}\) Nike \(\frac{\text {Produce}}{\longrightarrow}\) Acalme Sneaker
User \(\stackrel{\text {Purchase}}{\longrightarrow}\)Item\(\frac{\text {Produced}_{-} \mathrm{By}}{\longrightarrow}\) Brand \(\stackrel{\text {Produce}}{\longrightarrow}\)Item
Adversarial Actor-Critic for Path Finding
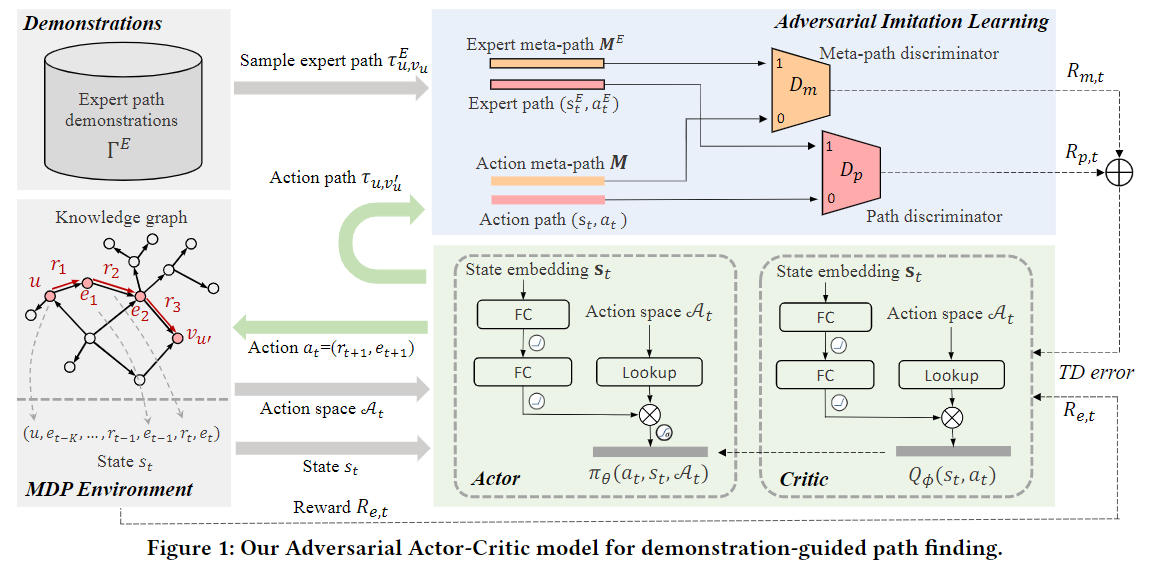
这个算法将actor-critic-based reinforcement learning和adversarial imitation learning相结合
MDP环境
用于通知actor它现在的搜索状态,以及可能采取的行为,同时对actor产生奖励
其定义为一个四元组\((\mathcal{S}, \mathcal{A}, \delta, \rho)\),
state
只考虑K步以内的entity和relation作为状态
action
所有能够与当前实体连接的下一个实体的集合
transition
\(s_{t+1}=\delta\left(s_{t}, a_{t}\right)\)
reward
只对最终状态进行奖励,对于中间的寻路过程不进行奖励
Actor
用于通过全连接网络来学习根据当前状态\(s_{t}\)以及当前所有的行动空间\(\mathcal{A}_{t}\),采取每一种行动的概率\(p\left(a_{t} \mid s_{t}, \mathcal{A}_{t}\right)\),用\(\pi_{\theta}\left(a_{t}, s_{t}, \mathcal{A}_{t}\right)\)来表示
学习过程如下:
\(h_{\theta}=\operatorname{ReLU}\left(W_{\theta, 1} s_{t}\right)\)
\(p\left(a_{t} \mid s_{t}, \mathcal{F}_{t}\right)=\pi_{\theta}\left(a_{t}, s_{t}, \mathcal{F}_{t}\right)=\frac{\mathbf{a}_{t} \cdot \operatorname{ReLU}\left(W_{\theta, 2} h_{\theta}\right)}{\sum a_{i} \in \mathcal{A}_{t} \mathbf{a}_{i} \cdot \operatorname{ReLU}\left(W_{\theta, 2} h_{\theta}\right)}\)
其中\(\mathbf{s}_{t}=\mathbf{u} \oplus \mathbf{e}_{t-K} \oplus \ldots \mathbf{e}_{t-1} \oplus \mathbf{r}_{t} \oplus \mathbf{e}_{t}\),不够k,用padding补齐
Adversarial Imitation Learning
由两个识别器组成,分别是 a path discriminator and a meta-path discriminator,分别用来识别actor产生的路径是否与path,以及meta-path相似
Path discriminator:用于识别path形成过程中的每一步是否与样本的path相似,计算公式如下:
\(h_{p}=\tanh \left(\mathbf{s}_{t} \oplus \mathbf{a}_{p, t}\right)\)
\(D_{p}\left(s_{t}, a_{t}\right)=\sigma\left(\beta_{p}^{T} \tanh \left(W_{p} h_{p}\right)\right)\),我们训练\(D_{p}\left(s_{t}, a_{t}\right)\),使得它的可以识别当前path片段与样例的相似程度
meta-path discriminator:用于在path最终形成时,识别当前path是否与样例的meta-path相似
对于meta-path的embedding\(\mathbf{M}=\mathbf{r}_{1} \oplus \mathbf{r}_{2} \oplus \ldots \mathbf{r}_{T}\),其学习公式如下:
\(\boldsymbol{h}_{m}=\tanh \left(\boldsymbol{W}_{m, 1} \mathbf{M}\right)\)
\(D_{m}(\mathbf{M})=\sigma\left(\boldsymbol{\beta}_{m}^{T} \tanh \left(\boldsymbol{W}_{m, 2} \boldsymbol{h}_{m}\right)\right)\)
Critic
用于建模来自MDP和两个识别器对于actor的奖励
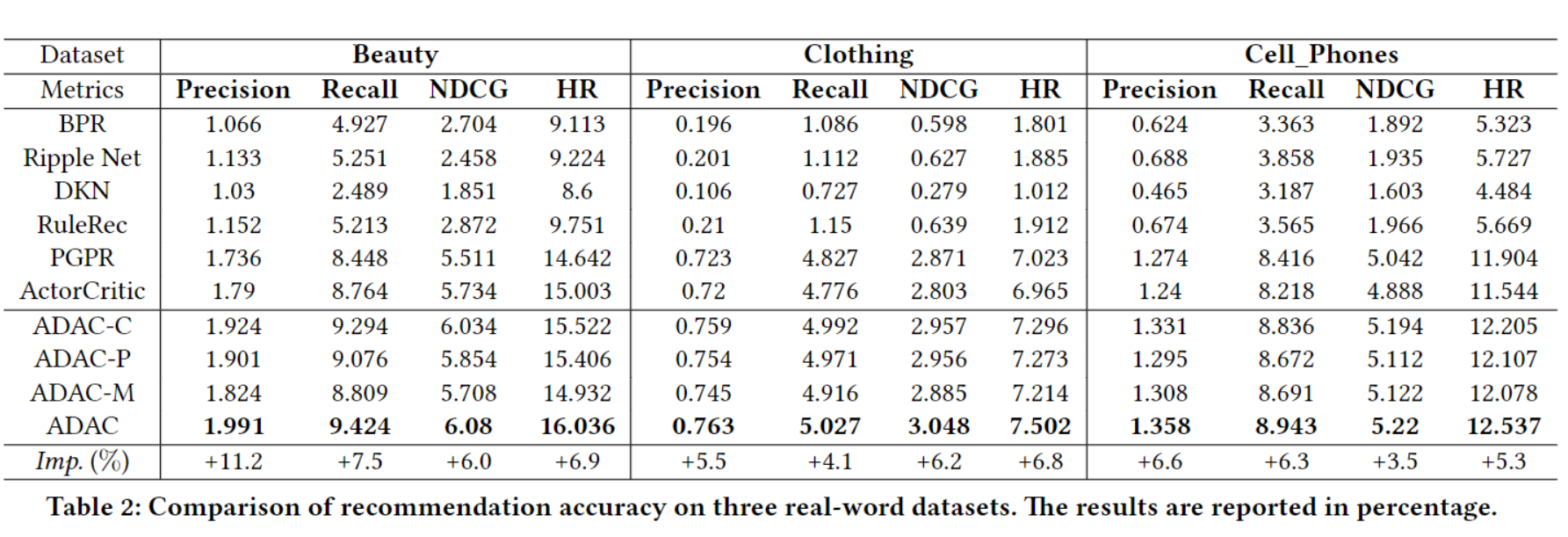
实验结果
Leveraging Demonstrations for Reinforcement Recommendation Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs 论文阅读